In an era where data is more valuable than gold, safeguarding digital assets against cyber threats has become a essential aspect of running a business.
In 2023 – 32% of businesses and 24% of charities reported experiencing cyber security breaches or attacks in the last 12 months, according to the Cyber Security Breaches Survey conducted by GOV.UK.
One significant step towards this is obtaining cybersecurity insurance. Cybersecurity insurance, or cyber liability insurance, is designed to mitigate financial losses from a variety of cyber incidents including data breaches, ransomeware attacks, and network damage.
Cyber insurance acts as a safety net, helping businesses cope with the aftermath of cyber incidents which might otherwise have devastating financial implications.
Understanding cybersecurity insurance is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring a swift recovery post-incident.
There has been a massive shift in cyber insurance. The industry is still young than as both underwriters and companies are still navigating how to pair policies with businesses.
Here are 9 facts and stats about cyber insurance worth sharing with your clientele as you plan your marketing strategy to market cyber insurance.
About the Cyber Insurance Market
1. Cyber Insurance is a Growing Trend:
The global cyber insurance market is projected to reach a size of roughly 22 billion U.S. dollars by 2025, which would be a doubling in size from its current state.
The global cyber insurance market is projected to reach a size of roughly $22 billion U.S. dollars by 2025, which would be a doubling in size from its current state.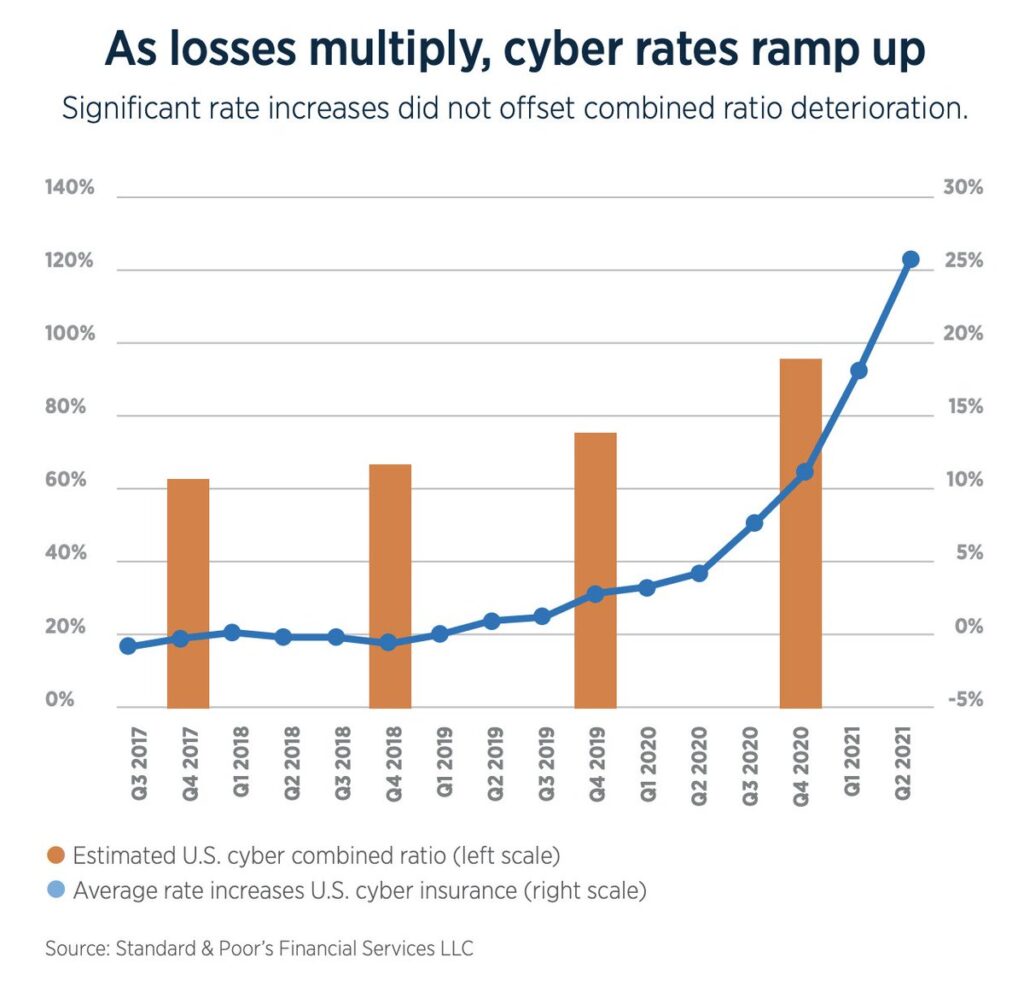
2. The Cost of Ransomware is Growing
According to cyber insurance broker Embroker – the average cost of a single ransomware attack is $1.85 million.
Barts Health NHS Trust, The City of Dallas, and YUM! Brands (Parent company of KFC, Pizza Hut, and Taco Bell) have all been hit with a ransomware attack in 2023
3. SMBs are the Main Targets For criminals:
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) are often deemed more vulnerable to cyber-attacks, and many are turning to cyber insurance for added protection.
As of 2023, over 72 percent of businesses worldwide were affected by ransomware attacks.
4. Nation State Attacks Do Not Qualify
Lloyd’s of London in particular has told its insurance groups worldwide that starting March 31, 2023, new or updated cyber insurance policies won’t cover nationstate attacks. They made this change because such attacks can be a big risk to the insurance market. They’ve also made a similar rule for losses caused by war, unless there’s a special exception noted in the policy.
5. Regulatory Environment:
The regulatory environment surrounding cyber insurance is still evolving, with standards and requirements potentially differing across regions.
6. Cyber Insurance is Becoming a Standard:
More enterprises are requiring their vendors and partners to carry cyber insurance, making it a standard practice in some industries. The reasoning is to mitigate risk on both sides.
7. Incident Response
Many cyber insurance policies offer incident response services, helping businesses effectively navigate the aftermath of a cyber event.
8. Cyber Hygiene Can Reduce Premiums:
Effective cyber hygiene practices can potentially lower premiums and are encouraged by insurers to minimize risk.
9. Breach Response and First Party Insurance are the Most Popular Types Of Cyber Insurance
Breach Response Insurance provides support in the aftermath of a data breach, covering the costs of notification, public relations efforts, and legal consultations to navigate regulatory requirements.
It’s a lifeline for businesses, ensuring they have the necessary resources to manage a breach effectively.
On the other hand, First-Party Insurance covers the financial losses a company may face due to cyber incidents, such as business interruption, data recovery, and cyber extortion costs. This insurance is crucial for maintaining financial stability and ensuring business continuity in the face of cyber threats.



